

You cannot use the INTERVAL data type for columns in Amazon Redshift tables. If you do not specify a datepart or literals, the interval value represents seconds.Ĭreate Redshift Table with Interval Data Type
 In Redshift, interval literals must include the units like ‘1 days’. The following table compares the Amazon Redshift data types and the transformation data types: Signed two-byte integer. You can specify the quantity value as a fraction. Here, is the Amazon Redshift data type alias. Redshift allows you to specify interval qualifiers such as years, months, weeks, days, etc. You can implement an INTERVAL data type in a same or slightly different way compared to other databases. Redshift interval literalsīelow are the Redshift interval literals: Supported Interval Description For examples, INTERVAL ‘1 days, 2 hours, 59 minutes’.Ībbreviations and plurals of each unit are also supported for example: 5 s, 5 second, and 5 seconds are equivalent intervals. You can form a precise interval type by combining multiple units. All intervals are the same, and can contain values of any combination of units.Īn interval is expressed as a combination of the INTERVAL keyword with a numeric quantity and a supported datepart for example: INTERVAL ‘1 days’ or INTERVAL ’10 minutes’. Redshift accepts the interval syntax, but ignores the unit specification. You can use these interval literals in conditions and calculations that involve date-time expressions.
In Redshift, interval literals must include the units like ‘1 days’. The following table compares the Amazon Redshift data types and the transformation data types: Signed two-byte integer. You can specify the quantity value as a fraction. Here, is the Amazon Redshift data type alias. Redshift allows you to specify interval qualifiers such as years, months, weeks, days, etc. You can implement an INTERVAL data type in a same or slightly different way compared to other databases. Redshift interval literalsīelow are the Redshift interval literals: Supported Interval Description For examples, INTERVAL ‘1 days, 2 hours, 59 minutes’.Ībbreviations and plurals of each unit are also supported for example: 5 s, 5 second, and 5 seconds are equivalent intervals. You can form a precise interval type by combining multiple units. All intervals are the same, and can contain values of any combination of units.Īn interval is expressed as a combination of the INTERVAL keyword with a numeric quantity and a supported datepart for example: INTERVAL ‘1 days’ or INTERVAL ’10 minutes’. Redshift accepts the interval syntax, but ignores the unit specification. You can use these interval literals in conditions and calculations that involve date-time expressions. 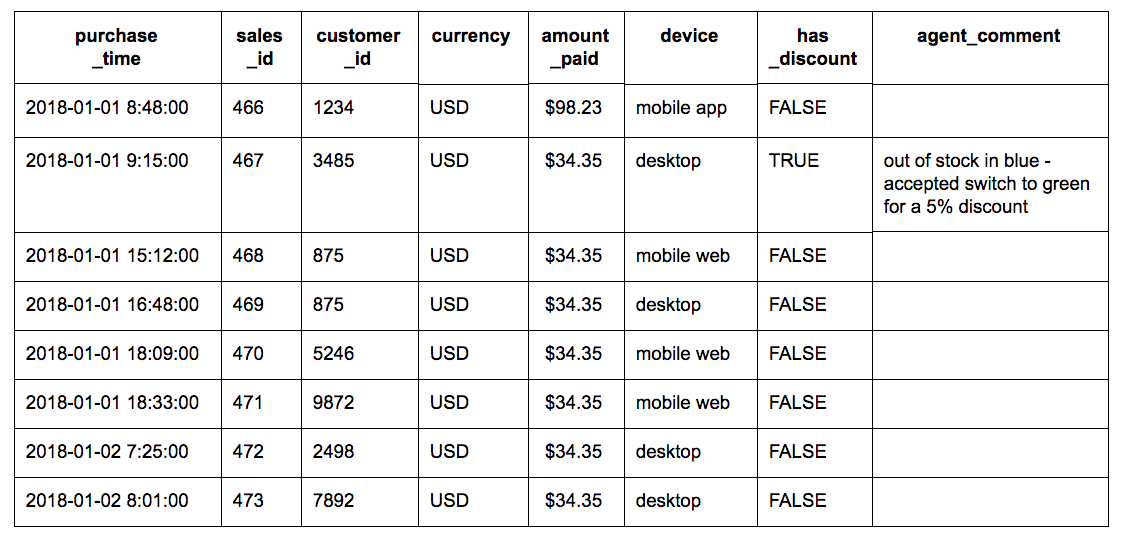
Use an interval literal to identify specific periods of time, such as 10 hours or 6 days.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
